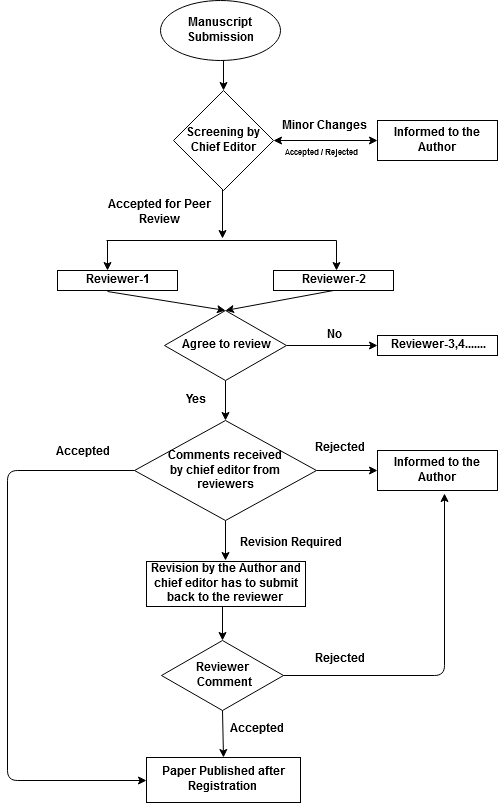
The peer review process for IJELS(English Literature Journal | Social Sciences Journal) Research journal is essentially a quality control mechanism to gives its best publication. This is the process by which field experts evaluate the proposed works, and its application to ensure a high quality of published work. However, the peer reviewers do not make the decision to reject or accept the articles but they recommend a decision. At peer-reviewed journal, decision-making authority rests solely with the journal’s editorial board.
Normally there are three types of peer review processing for journal publication
- Single-blind: names of reviewers are not disclosed to authors
- Double-blind: names of reviewers and authors are not disclosed to each other
- Open peer review: Names of authors and reviewers are disclose to each other
IJELS research journal is a double blind-reviewed journal. Normally, we choose a minimum of 2 reviewers for the peer review. Peer reviewers are experts in their field. We usually build a pool of peer reviewers that have a good record of producing high-quality reviews. Or we scan the bibliography to identify potential reviewers or contact researchers they met at conferences and seminars for review processing.
The Journal editorial boards consider the report or feedbacks provided by the peer reviewers in an article and take a decision. The most common decisions, which we made for an article publication, are:
- Accept the article without any changes (acceptance): publish the article in its original form as provided by the author.
- Accept the article with minor revisions (acceptance): asks the author to make small corrections and then publish the article.
- Accept the article after major revisions (modification): ask the authors to make the changes suggested by the reviewers and/or editors: after revision publish the article.
- Revise and resubmit the article (conditional- rejection): the journal fails to accept the article in the current round and willing to reconsider the article in another round of decision making after the authors make major changes in the article as suggested.
- reject the article (rejection): the journal will not publish the article or reconsider it even if the authors make major revisions in the article.
Paper Publishing Process (Double Blind Peer Review)
 Submit Your Paper Now!!
Submit Your Paper Now!!



















